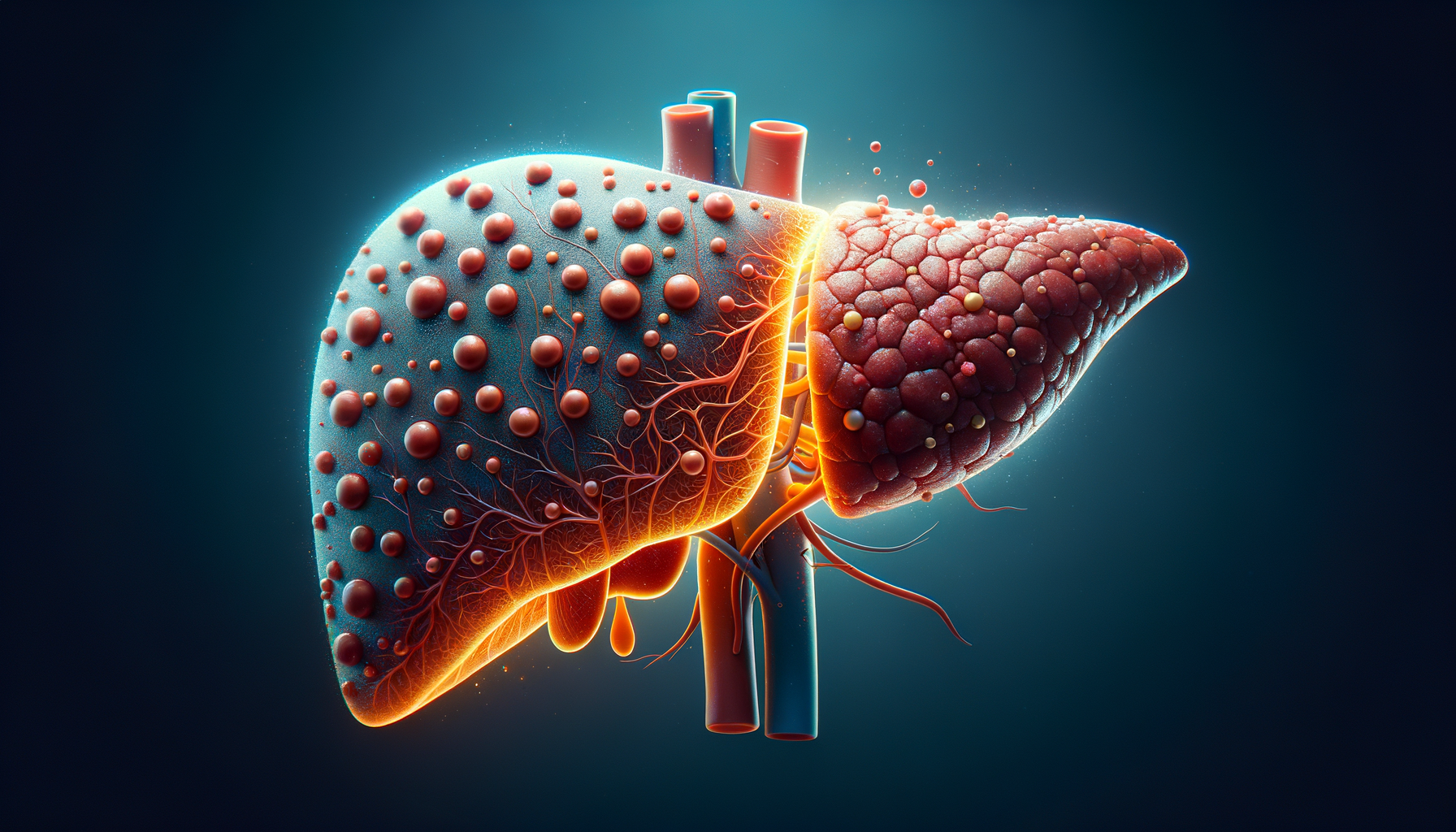
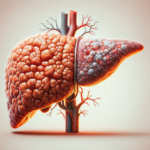
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease, a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, is becoming increasingly common. It can be broadly categorized into two types: Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD) and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). While AFLD is directly linked to excessive alcohol consumption, NAFLD occurs in individuals who consume little to no alcohol. The latter is often associated with metabolic syndrome, which includes conditions like obesity, type 2 diabetes, and high cholesterol.
Despite its prevalence, fatty liver disease often goes undiagnosed because it typically presents no symptoms in its early stages. This silent progression makes it a stealthy condition that can lead to more serious liver damage if left unchecked. Understanding the risk factors and early signs is crucial for prevention and management. Common risk factors include obesity, insulin resistance, and high triglyceride levels. It’s important to note that you don’t have to be overweight to be at risk. Fatty liver disease can affect individuals of all body types.
Early detection through regular health check-ups can help manage and even reverse the condition. Blood tests, imaging studies like ultrasound, and sometimes liver biopsy are used to diagnose fatty liver disease. Regular monitoring and lifestyle changes are key to preventing progression to more severe liver conditions such as cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The silent nature of fatty liver disease means that many people are unaware they have it until it is discovered during tests for other conditions. However, as the disease progresses, some symptoms may start to appear, including fatigue, abdominal discomfort, and unexplained weight loss. These symptoms are often vague and can be easily attributed to other health issues, which complicates timely diagnosis.
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Blood tests can reveal elevated liver enzymes, which may indicate liver inflammation. Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI can detect fat accumulation in the liver. In some cases, a liver biopsy may be performed to assess the extent of liver damage.
It’s crucial to learn the early signs and to consult healthcare professionals if you suspect you might be at risk. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes and prevent further liver damage. Regular health check-ups and being proactive about liver health can make a real difference in managing this condition.
Causes and Risk Factors
Fatty liver disease is influenced by a variety of factors, both genetic and lifestyle-related. Key causes include obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. These conditions lead to the accumulation of fat in liver cells, which can eventually cause liver inflammation and damage. Genetics also play a role, as certain genetic mutations can increase susceptibility to fatty liver disease.
Lifestyle factors such as diet and physical activity levels are significant contributors. A diet high in saturated fats, sugars, and refined carbohydrates can exacerbate fat buildup in the liver. Conversely, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help mitigate this risk. Regular physical activity aids in maintaining a healthy weight and improving insulin sensitivity, both of which are crucial in managing and preventing fatty liver disease.
Other risk factors include certain medical conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. It’s important to note that while these factors increase the risk, fatty liver disease can also occur in individuals without these conditions. Therefore, understanding and addressing these risk factors is essential in preventing and managing fatty liver disease.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes
Taking control of your liver health involves adopting preventive measures and making lifestyle changes. These small changes can have a significant impact on your liver health and overall well-being. One of the most effective ways to prevent fatty liver disease is through a balanced diet and regular exercise. Aim for a diet low in saturated fats and sugars, and rich in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Incorporating regular physical activity into your routine is equally important. Activities such as walking, cycling, or swimming can help maintain a healthy weight and improve insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, as recommended by health experts.
Other preventive measures include regular monitoring of liver health through blood tests and imaging studies, especially for individuals with risk factors. Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and managing underlying health conditions such as diabetes and high cholesterol are also crucial in preventing fatty liver disease. By taking these proactive steps, you can significantly reduce your risk and protect your liver health.
Treatment and Management Strategies
While there is no specific medication for fatty liver disease, treatment focuses on managing underlying conditions and making lifestyle modifications. Weight loss is often recommended, as it can reduce liver fat, inflammation, and fibrosis. Losing even a small percentage of body weight can have a positive impact on liver health.
Dietary changes play a vital role in managing fatty liver disease. A Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, is often recommended. Reducing sugar intake, particularly fructose, is also beneficial. Consulting a dietitian can provide personalized dietary advice that aligns with your health goals.
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage conditions such as diabetes or high cholesterol. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential to monitor liver health and adjust treatment plans as needed. By embracing these management strategies, individuals with fatty liver disease can improve their liver health and overall quality of life.