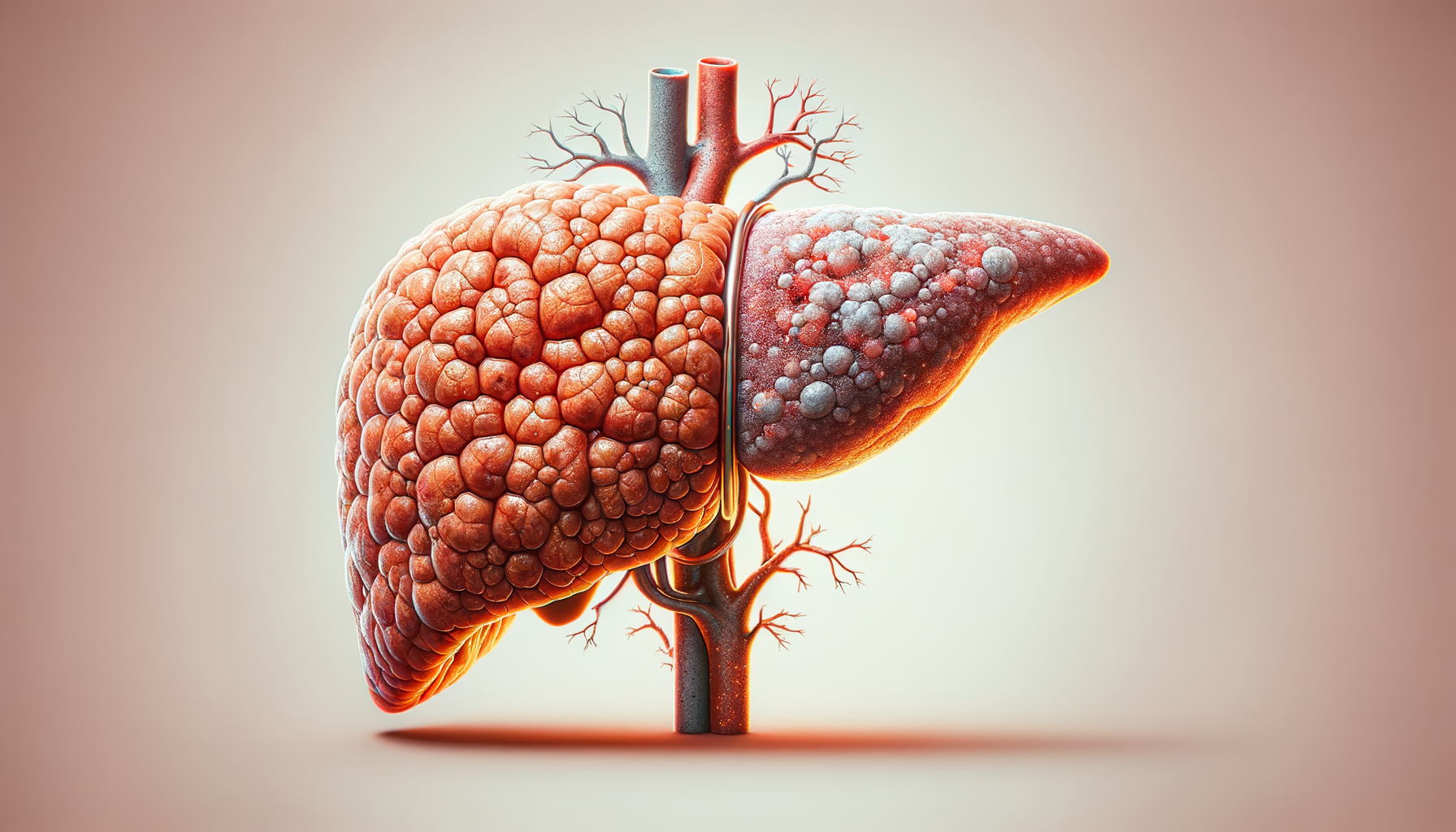
Understanding Fatty Liver: A Silent Health Concern
Fatty liver disease, often referred to as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fat in the liver cells. While it might sound benign, this condition can lead to more severe liver issues if left unchecked. The liver, a vital organ responsible for numerous functions such as detoxification, protein synthesis, and chemical production necessary for digestion, can become compromised when overloaded with fat. The condition is surprisingly common and can affect individuals who are not overweight, challenging the common misconception that it is solely linked to obesity. Recognizing the early warning signs is crucial, as fatty liver often develops quietly, with few or no clear symptoms.
There are two primary types of fatty liver disease: alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The latter is more prevalent and is not caused by alcohol consumption but rather by factors such as poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and genetic predisposition. NAFLD can progress to more severe liver damage, including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Understanding the risk factors and early signs can empower individuals to take proactive steps in managing their liver health.
Risk Factors and Causes of Fatty Liver
The causes of fatty liver disease are multifaceted, involving a combination of lifestyle, genetic, and environmental factors. One of the most significant contributors is diet, particularly diets high in saturated fats and sugars, which can lead to obesity—a well-known risk factor. However, it’s important to note that fatty liver can develop in individuals who are not overweight, emphasizing the importance of understanding other contributing factors.
Sedentary lifestyle choices also play a critical role in the development of fatty liver. Lack of physical activity can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance, both of which are linked to the accumulation of liver fat. Additionally, certain medical conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and metabolic syndrome increase the risk. Genetic predisposition can also influence the likelihood of developing fatty liver, with some individuals being more susceptible due to their genetic makeup.
While the condition is often associated with adults, it is increasingly being diagnosed in children, underscoring the need for awareness and preventive measures across all age groups. By identifying and addressing these risk factors, individuals can make informed lifestyle choices that support liver health and reduce the risk of developing fatty liver disease.
Symptoms and Diagnosis: Recognizing Fatty Liver Early
One of the challenges in managing fatty liver disease is its tendency to develop silently. Many individuals with fatty liver may not experience noticeable symptoms, making early diagnosis difficult. However, there are subtle signs that can indicate the presence of the condition. These may include fatigue, discomfort or pain in the upper right abdomen, and unexplained weight loss. It’s crucial for individuals to pay attention to these signs, especially if they have known risk factors.
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, and imaging tests. Blood tests can reveal elevated liver enzymes, which may suggest liver inflammation. Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI can help visualize fat accumulation in the liver. In some cases, a liver biopsy may be necessary to assess the extent of liver damage and rule out other conditions. Early diagnosis is essential for effective management and to prevent progression to more severe liver diseases.
Regular check-ups and liver function tests are recommended for individuals at risk, as they can help detect changes in liver health before significant damage occurs. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can work with healthcare providers to monitor liver health and implement necessary lifestyle changes.
Managing and Preventing Fatty Liver Through Lifestyle Changes
While there is no specific medication for fatty liver disease, lifestyle modifications can significantly impact its management and prevention. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight are foundational strategies for reducing liver fat and improving overall liver health.
Dietary changes should focus on reducing saturated fats and sugars while incorporating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. The Mediterranean diet, rich in healthy fats from sources like olive oil and nuts, has been shown to benefit liver health. Regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercises and strength training, can help reduce liver fat and improve insulin sensitivity.
In addition to diet and exercise, limiting alcohol consumption is crucial, as alcohol can exacerbate liver damage. For those with existing liver conditions, complete abstinence may be necessary. Regular monitoring of liver health through medical check-ups can help track progress and make necessary adjustments to lifestyle habits. By adopting these changes, individuals can take control of their liver health and reduce the risk of fatty liver disease.
The Future of Fatty Liver Research and Treatment
Research into fatty liver disease is ongoing, with scientists exploring new treatment options and preventive measures. Advances in medical technology and a deeper understanding of the condition’s underlying mechanisms are paving the way for innovative solutions. Current studies are investigating the role of gut microbiota, genetic factors, and novel pharmaceuticals in the development and management of fatty liver disease.
Emerging therapies aim to target specific pathways involved in liver fat accumulation and inflammation. These include medications that improve insulin sensitivity, reduce oxidative stress, and promote liver regeneration. Additionally, researchers are exploring the potential of lifestyle interventions, such as personalized nutrition and exercise programs, to provide tailored solutions for individuals at risk.
As research progresses, the hope is to develop more effective strategies for diagnosing, treating, and ultimately preventing fatty liver disease. By staying informed about these advancements, individuals can be better equipped to make informed decisions about their liver health and contribute to ongoing efforts to combat this silent yet significant health concern.