Understanding COPD: A Chronic Challenge
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) represents a group of progressive lung conditions that obstruct airflow and make breathing difficult. It primarily includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis, conditions that often coexist. The significance of understanding and managing COPD cannot be overstated, as it is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Approximately 16 million Americans have been diagnosed with COPD, with many more likely undiagnosed. The disease is characterized by symptoms such as chronic cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, and frequent respiratory infections. These symptoms severely impact the quality of life, making everyday activities a challenge. Knowledge about COPD, its causes, and its management is crucial for patients and caregivers alike to improve life quality and reduce the disease’s progression.
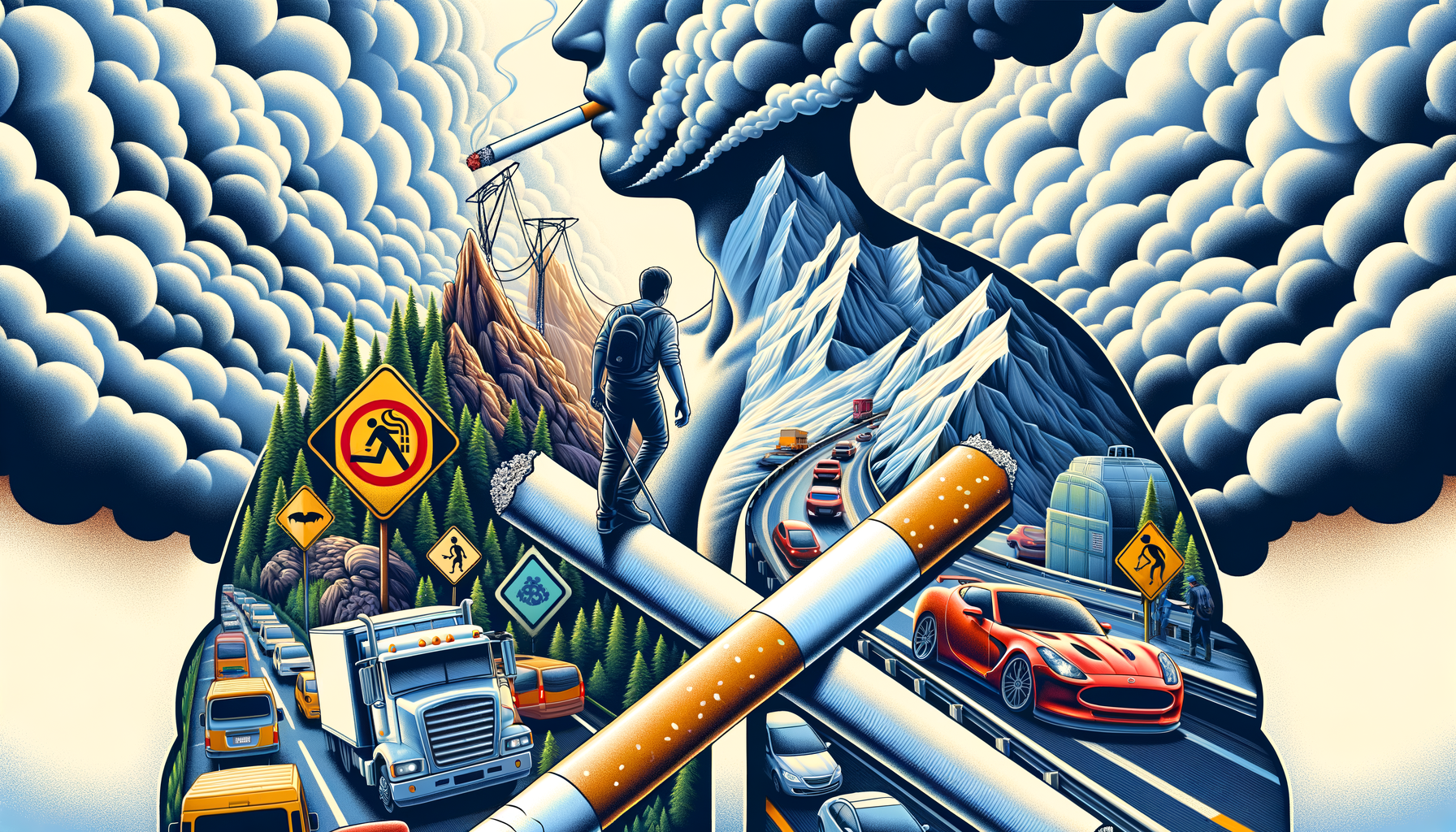
Common Triggers: Activities to Watch Out For
For individuals living with COPD, certain activities can exacerbate symptoms, leading to discomfort and health complications. Understanding these triggers is essential for effective disease management. Common activities that may worsen COPD symptoms include:
- Exposure to Pollutants: Activities that involve exposure to smoke, dust, or strong fumes, such as cooking without proper ventilation or being in a smoky environment, can aggravate COPD symptoms.
- Physical Exertion: While regular exercise is beneficial, overexertion can lead to breathlessness and fatigue. It’s important to balance activity levels with adequate rest.
- Cold Weather Activities: Cold air can constrict airways, making breathing more difficult. Outdoor activities in cold weather should be limited, and protective measures like wearing scarves over the mouth and nose can help.
- Stressful Situations: High-stress activities or environments can lead to anxiety and breathlessness, further complicating COPD management.
Avoiding these triggers, when possible, can help in maintaining better control over COPD symptoms.
Diet and Nutrition: Fueling the Body Right
Nutrition plays a vital role in managing COPD. A balanced diet can help maintain energy levels, support immune function, and improve lung health. Patients with COPD often experience weight loss and muscle wasting, making nutritional support essential.
Key dietary considerations for COPD patients include:
- High-Calorie, High-Protein Diet: To counteract weight loss and muscle wasting, a diet rich in calories and protein is recommended. This includes lean meats, dairy products, and legumes.
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Foods high in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, can help combat oxidative stress in the lungs.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated helps thin mucus, making it easier to expel. However, fluid intake should be balanced to prevent fluid overload.
Working with a dietitian can be beneficial in creating a personalized nutrition plan that meets the specific needs of those with COPD.
Exercise: Finding the Right Balance
Exercise is a double-edged sword for COPD patients. While physical activity is essential for maintaining muscle strength and cardiovascular health, overexertion can lead to breathlessness and exacerbate symptoms. The key is finding the right balance.
Safe exercise tips for COPD patients include:
- Low-Impact Exercises: Activities like walking, cycling, and swimming are generally well-tolerated and can improve fitness levels without causing excessive strain.
- Breathing Techniques: Incorporating breathing exercises such as pursed-lip breathing can help manage breathlessness during physical activity.
- Regular Breaks: Taking frequent breaks during exercise sessions can help prevent fatigue and breathlessness.
Consulting a healthcare provider before starting any exercise regimen is crucial to ensure safety and effectiveness.
The Role of Medication and Treatment Plans
Medication and treatment plans are the cornerstone of COPD management. They aim to control symptoms, improve quality of life, and slow disease progression. Common medications used in COPD management include bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors.
Effective management involves:
- Adherence to Medication: Consistently taking prescribed medications as directed by healthcare professionals is crucial for maintaining symptom control.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups with healthcare providers help monitor disease progression and adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Vaccinations: Staying up-to-date with vaccinations, such as the flu and pneumonia vaccines, can help prevent respiratory infections that can worsen COPD.
Collaborating with healthcare providers to create and adhere to a personalized treatment plan is essential for managing COPD effectively.